Apoptosis-mediated antiproliferation of A549 lung cancer cells mediated by Eugenia aquea leaf compound 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-methoxy-3′,5′-dimethylchalcone and its molecular interaction with caspase receptor in molecular docking simulation.
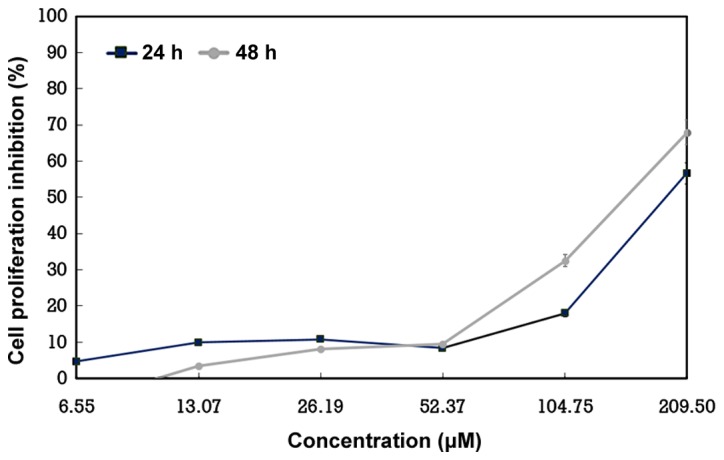
In a earlier research, 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-methoxy-3′,5′-dimethylchalcone (ChalcEA) remoted from the leaves of Eugenia aquea was reported to inhibit proliferation of the breast adenocarcinoma MCF7 cell line and to advertise apoptosis by way of activation of poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase protein. The current research aimed to guage the inhibitory impact of ChalcEA on the proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells […]